|
|
 |
 HOME > Field of business > Incinerator plant introduction HOME > Field of business > Incinerator plant introduction |
 |
| |
|
| |
 |
| |
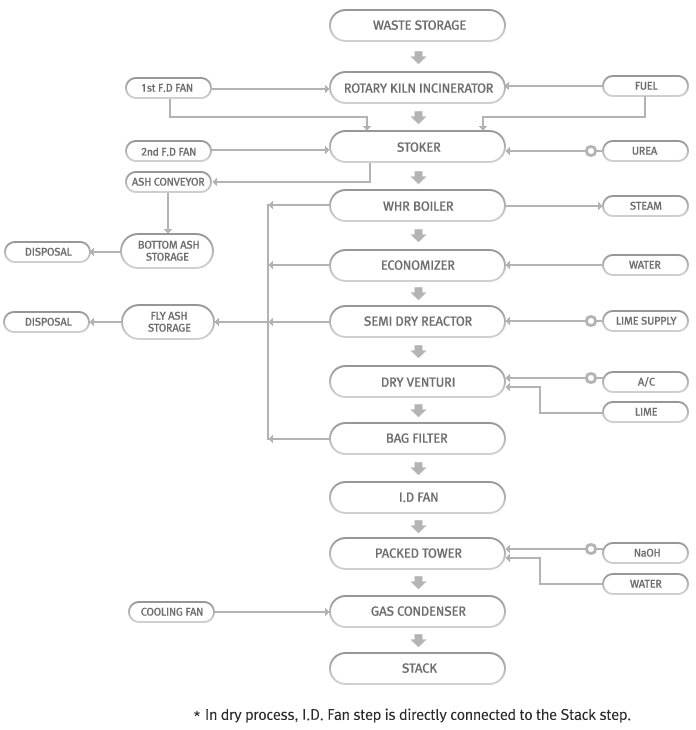
| Horizontal rotated cylindrical typed Rotary kiln has inclination angle of 2~5˚, through which inserted waste is passed, dried and combusted, and the remaining of waste not combusted is completely combusted at the stoker incinerator installed at the end of rotary kiln. This Rotary kiln type makes 60~70% of waste combusted, and the remaining not combusted, 30~40%, is combusted at the stoker area. Combustion air needed for each combustion step is supplied to the Rotary kiln and down area of stoker evenly, and for complete combustion secondary air with high speed is injected into the upper area of stoker.
|
| |
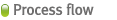 |
| |
 |
| |
 |
 |
| |
 |
 Liquid, solid waste both of them can be incinerated, and mixed incineration is also possible. Liquid, solid waste both of them can be incinerated, and mixed incineration is also possible.
 Not obstructed by melting status material. Not obstructed by melting status material.
 Detention time of waste can be controlled according to the control of rotating speed of incinerator. Detention time of waste can be controlled according to the control of rotating speed of incinerator.
 Good for the destruction of noxious material due to the operation at high temperature over 1400℃ Good for the destruction of noxious material due to the operation at high temperature over 1400℃
 Erection cost high. (The less treatment capacity, the more expensive) Erection cost high. (The less treatment capacity, the more expensive)
 Big air discharge in incinerator, so big amount of excess air is needed often. Big air discharge in incinerator, so big amount of excess air is needed often.
 Dust load factor high in the control system of air pollutant. Dust load factor high in the control system of air pollutant.
 Heat efficiency low relatively. Heat efficiency low relatively.
|
| |
| |
 |
 Industrial waste Industrial waste
 Flame retarding waste fluid mixed-waste Flame retarding waste fluid mixed-waste
 Sludge mixed-waste Sludge mixed-waste
|
| |
| |
| |
|

